Beijing Betavolt New Energy Technology Company Ltd has announced a groundbreaking achievement in the field of energy technology, claiming the successful development of a miniature atomic energy battery that can generate power continuously for 50 years without the need for charging or maintenance. The company aims to introduce this innovation to the mass market, marking a significant milestone in the field of sustainable and long-lasting power solutions.
What is Atomic Battery Technology?
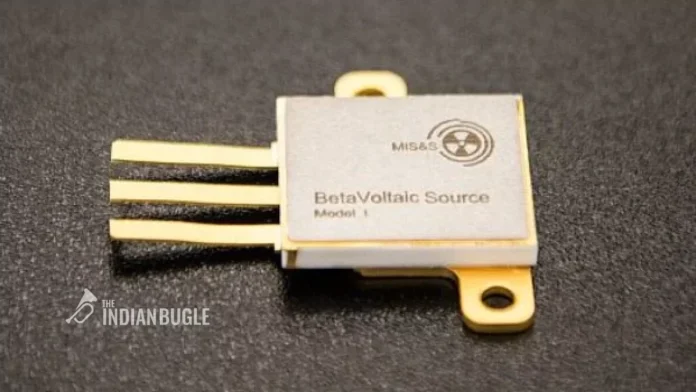
Betavolt’s achievement revolves around the development of the BV100 battery, utilizing nuclear isotope decay technology combined with China’s first diamond semiconductor module. This breakthrough enables the miniaturization of atomic energy batteries, challenging conventional ideas associated with power generation.
Atomic energy batteries, also known as nuclear batteries or radioisotope batteries, operate by harnessing the energy released through the decay of nuclear isotopes. These batteries convert this energy into electrical power through semiconductor converters, providing a stable and autonomous source of electricity.
The BV100 battery boasts a unique design featuring a 10-micron-thick single-crystal diamond semiconductor, with a 2-micron-thick nickel-63 sheet placed between two diamond semiconductor converters. This design allows the conversion of radioactive decay energy into electrical current, creating an independent unit. Moreover, Betavolt highlights the modular nature of its nuclear batteries, which can be composed of numerous independent unit modules, allowing for various sizes and capacities to be manufactured through series and parallel configurations.
Betavolt envisions its nuclear batteries catering to diverse applications, including aerospace, AI equipment, medical devices, micro-electromechanical systems, advanced sensors, small drones, and micro-robots. The company suggests that, if regulations permit, mobile phones may never need charging, and drones with limited flight times could operate continuously.
BV100: The First Mass-Produced Nuclear Battery
The BV100 is set to be the world’s first mass-produced nuclear battery. Compact in size, measuring 15mm by 15mm and 5mm thick, the BV100 can generate 100 microwatts with a voltage of 3V. Betavolt plans to introduce a 1-watt battery variant in 2025, showcasing the scalability and adaptability of their atomic energy battery technology.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Betavolt emphasizes the safety of its atomic energy battery, stating that it is devoid of external radiation, making it suitable for use in medical devices like pacemakers, artificial hearts, and cochlear implants. Additionally, the company asserts that these batteries are environmentally friendly. After the decay period, the nickel-63 isotope transforms into a stable, non-radioactive isotope of copper, posing no threat or pollution to the environment.
Future Developments and Research
Looking ahead, Betavolt plans to continue its research by exploring isotopes such as strontium-90, promethium-147, and deuterium. The aim is to develop atomic energy batteries with higher power output and extended service life, ranging from 2 to 30 years.
In summary, Betavolt’s groundbreaking nuclear battery technology opens up new possibilities for long-lasting and sustainable power solutions, with potential applications across various industries. As the BV100 enters mass production, the company paves the way for a future where compact and reliable atomic energy batteries become integral components of our everyday devices.